Database
This document aims to guide users through the installation and testing of a multi-node Docker-based Elasticsearch database cluster. It provides detailed steps for setting up the cluster and verifying its functionality.
Elastic Multi-Node Docker Installation Guide
Core Conclusion
This guide demonstrates the deployment of a multi-node Elasticsearch cluster (including Kibana) using Docker. By splitting configuration files, synchronizing certificates, and setting environment variables, cross-node deployment is achieved, resulting in a healthy and functional cluster environment.
1. Environment Preparation
-
Basic Requirements:
- Docker: 24.0.7+
- Docker Compose: v2.21.0+
- Operating System: Linux/amd64
-
Image Details:
- Elasticsearch: 8.15.2
- Kibana: 8.15.2
-
Node Planning:
At least two nodes are required. In this example, we use two nodes:- Node 1: IP address
ip1, hosting Elasticsearch instancees01and Kibana. - Node 2: IP address
ip2, hosting Elasticsearch instancees02.
- Node 1: IP address
2. Pre-Deployment Preparation
1. Directory and Permission Configuration (All Nodes)
- Create Mount Directories by Node Role:
- Node 1: Create
/opt/data/{es01,kibana} - Node 2: Create
/opt/data/es02
- Node 1: Create
- Set Directory Permissions:
Execute the following command to set permissions, ensuring compatibility with the non-root user (ID 1000) inside the container:chown -R 1000:1000 /opt/data/<directory>
2. Configuration File Preparation (Node 1 First)
-
Create
.envFile:
Define core parameters such as Elastic and Kibana passwords, cluster name, version, ports, and memory limits. Below is an example:# Password for the 'elastic' user (at least 6 characters) ELASTIC_PASSWORD=1qazXSW@ # Password for the 'kibana_system' user (at least 6 characters) KIBANA_PASSWORD=1qazXSW@ # Version of Elastic products STACK_VERSION=8.15.2 # Set the cluster name CLUSTER_NAME=es-cluster # Set to 'basic' or 'trial' to automatically start the 30-day trial LICENSE=basic #LICENSE=trial # Port to expose Elasticsearch HTTP API to the host ES_PORT=9200 #ES_PORT=127.0.0.1:9200 # Port to expose Kibana to the host KIBANA_PORT=5601 #KIBANA_PORT=80 # Increase or decrease based on the available host memory (in bytes) MEM_LIMIT=17179869184 # Project namespace (defaults to the current folder name if not set) #COMPOSE_PROJECT_NAME=myproject -
Create
docker-compose.yamlFile:
Include the following services:setup: For certificate generation.es01: Elasticsearch instance.kibana: Kibana instance.
Configure mount directories, environment variables, and network modes as needed. Below is an example:
version: "3" services: setup: image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:${STACK_VERSION} volumes: - ./certs:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certs user: "0" command: > bash -c ' if [ x${ELASTIC_PASSWORD} == x ]; then echo "Set the ELASTIC_PASSWORD environment variable in the .env file"; exit 1; elif [ x${KIBANA_PASSWORD} == x ]; then echo "Set the KIBANA_PASSWORD environment variable in the .env file"; exit 1; fi; if [ ! -f config/certs/ca.zip ]; then echo "Creating CA"; bin/elasticsearch-certutil ca --silent --pem -out config/certs/ca.zip; unzip config/certs/ca.zip -d config/certs; fi; if [ ! -f config/certs/certs.zip ]; then echo "Creating certs"; echo -ne \ "instances:\n"\ " - name: es01\n"\ " dns:\n"\ " - es01\n"\ " ip:\n"\ " - ip1\n"\ " - name: es02\n"\ " dns:\n"\ " - es02\n"\ " ip:\n"\ " - ip2\n"\ > config/certs/instances.yml; bin/elasticsearch-certutil cert --silent --pem -out config/certs/certs.zip --in config/certs/instances.yml --ca-cert config/certs/ca/ca.crt --ca-key config/certs/ca/ca.key; unzip config/certs/certs.zip -d config/certs; fi; echo "Setting file permissions" chown -R root:root config/certs; find . -type d -exec chmod 750 \{\} \;; find . -type f -exec chmod 640 \{\} \;; echo "Waiting for Elasticsearch availability"; until curl -s --cacert config/certs/ca/ca.crt https://ip1:9200 | grep -q "missing authentication credentials"; do sleep 30; done; echo "Setting kibana_system password"; until curl -s -X POST --cacert config/certs/ca/ca.crt -u "elastic:${ELASTIC_PASSWORD}" -H "Content-Type: application/json" https://ip1:9200/_security/user/kibana_system/_password -d "{\"password\":\"${KIBANA_PASSWORD}\"}" | grep -q "^{}"; do sleep 10; done; echo "All done!"; ' healthcheck: test: ["CMD-SHELL", "[ -f config/certs/es01/es01.crt ]"] interval: 1s timeout: 5s retries: 120 es01: depends_on: setup: condition: service_healthy image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:${STACK_VERSION} volumes: - ./certs:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certs - /opt/data/es01:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data environment: - node.name=es01 - cluster.name=${CLUSTER_NAME} - cluster.initial_master_nodes=es01,es02 - discovery.seed_hosts=ip2 - ELASTIC_PASSWORD=${ELASTIC_PASSWORD} - bootstrap.memory_lock=true - xpack.security.enabled=true - xpack.security.http.ssl.enabled=true - xpack.security.http.ssl.key=certs/es01/es01.key - xpack.security.http.ssl.certificate=certs/es01/es01.crt - xpack.security.http.ssl.certificate_authorities=certs/ca/ca.crt - xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled=true - xpack.security.transport.ssl.key=certs/es01/es01.key - xpack.security.transport.ssl.certificate=certs/es01/es01.crt - xpack.security.transport.ssl.certificate_authorities=certs/ca/ca.crt - xpack.security.transport.ssl.verification_mode=certificate - xpack.license.self_generated.type=${LICENSE} restart: always network_mode: host ulimits: memlock: soft: -1 hard: -1 healthcheck: test: [ "CMD-SHELL", "curl -s -k --cacert config/certs/ca/ca.crt https://localhost:9200 | grep -q 'missing authentication credentials'", ] interval: 10s timeout: 10s retries: 120 kibana: depends_on: es01: condition: service_healthy image: docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:${STACK_VERSION} volumes: - ./certs:/usr/share/kibana/config/certs - /opt/data/kibana:/usr/share/kibana/data environment: - SERVERNAME=kibana - ELASTICSEARCH_HOSTS=https://ip1:9200 - ELASTICSEARCH_USERNAME=kibana_system - ELASTICSEARCH_PASSWORD=${KIBANA_PASSWORD} - ELASTICSEARCH_SSL_CERTIFICATEAUTHORITIES=config/certs/ca/ca.crt restart: always network_mode: host healthcheck: test: [ "CMD-SHELL", "curl -k -s -I http://localhost:5601 | grep -q 'HTTP/1.1 302 Found'", ] interval: 10s timeout: 10s retries: 120
3. Cluster Deployment Steps
1. Start es01 Node and Kibana
- Navigate to the configuration directory on the
es01node and start the services:docker compose up -d - Wait for the health checks to pass. You can verify the status using:
Ensure the status showsdocker compose psHealthyorStarted.
2. Synchronize Configuration Files to Other Nodes
- On the
es01node, execute the following command to synchronize the certificate directory and.envfile to the target node:scp -r certs/ .env target-node:/opt/compose/es/
3. Deploy es02 Node
- On the
es02node, create a dedicateddocker-compose.yamlfile. Retain only the configuration for the correspondingesservice, adapting parameters such as node name and discovery nodes. Below is an example:version: '3' services: es02: image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:${STACK_VERSION} volumes: - ./certs:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certs - /opt/data/es02/:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data environment: - node.name=es02 - cluster.name=${CLUSTER_NAME} - cluster.initial_master_nodes=es01,es02 - discovery.seed_hosts=ip1 - bootstrap.memory_lock=true - xpack.security.enabled=true - xpack.security.http.ssl.enabled=true - xpack.security.http.ssl.key=certs/es02/es02.key - xpack.security.http.ssl.certificate=certs/es02/es02.crt - xpack.security.http.ssl.certificate_authorities=certs/ca/ca.crt - xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled=true - xpack.security.transport.ssl.key=certs/es02/es02.key - xpack.security.transport.ssl.certificate=certs/es02/es02.crt - xpack.security.transport.ssl.certificate_authorities=certs/ca/ca.crt - xpack.security.transport.ssl.verification_mode=certificate - xpack.license.self_generated.type=${LICENSE} restart: always network_mode: host ulimits: memlock: soft: -1 hard: -1 healthcheck: test: [ "CMD-SHELL", "curl -s -k --cacert config/certs/ca/ca.crt https://localhost:9200 | grep -q 'missing authentication credentials'", ] interval: 10s timeout: 10s retries: 120 - Start the service on the
es02node:docker compose up -d - Wait for the health checks to pass. Ensure the status changes to
Healthy.
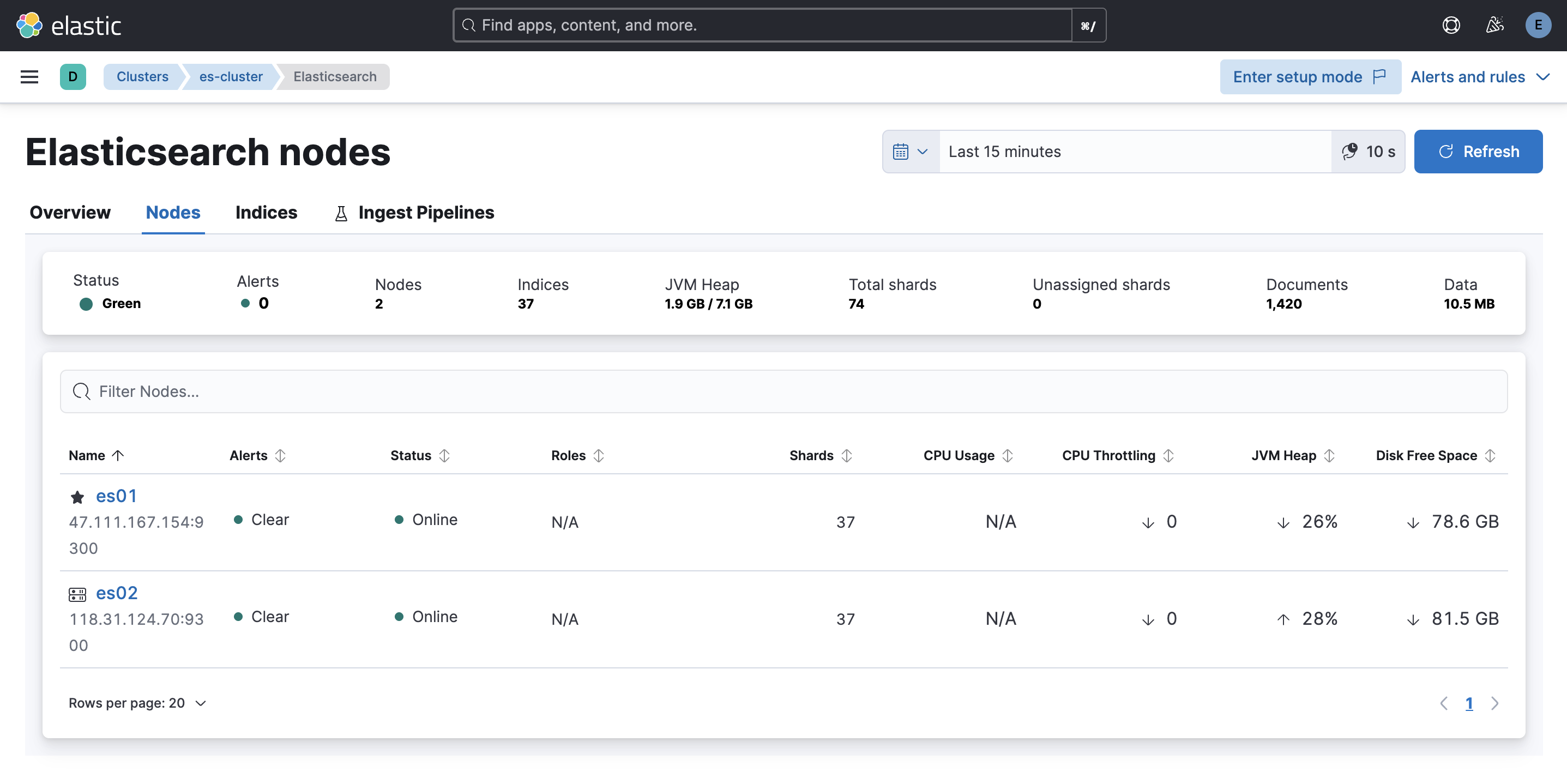
4. Cluster Verification
1. Verify Cluster Nodes
- Execute the following command to check if all nodes have successfully joined the cluster:
curl --user "elastic:<password>" -k https://<es01-node-IP>:9200/_cat/nodes?v
2. Check Cluster Health
- Run the following command to confirm the cluster status is
green(healthy):curl --user "elastic:<password>" -k https://<es01-node-IP>:9200/_cat/health?v
3. Access Kibana
- Open a browser and navigate to:
http://<es01-node-IP>:5601 - Log in using the
elasticusername and password to verify the availability of the Kibana visualization interface.
4. Client Read/Write Data Test
Below is an example Python script to test data read/write operations:
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
import ssl
import random
import time
import requests
requests.packages.urllib3.disable_warnings()
# Elasticsearch configuration
HOST = "https://ip1:9200" # Elasticsearch address
USER = "elastic" # Username
PASSWORD = "xxx" # Password
def create_client():
"""
Create an Elasticsearch client using self-signed certificates.
"""
try:
# Create Elasticsearch client
client = Elasticsearch(
hosts=[HOST],
basic_auth=(USER, PASSWORD),
verify_certs=False
)
print("Elasticsearch client created")
return client
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error creating Elasticsearch client: {e}")
raise
def main():
client = create_client()
# Test connection
try:
print("Testing connection...")
if client.ping():
print("Successfully connected to Elasticsearch!")
else:
print("Failed to connect to Elasticsearch!")
return
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error connecting to Elasticsearch: {e}")
return
# Example: Create index
index_name = "test-index"
try:
if not client.indices.exists(index=index_name):
client.indices.create(index=index_name)
print(f"Index {index_name} created")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error creating index: {e}")
return
# Example: Randomly write 10 documents
print("Writing data...")
for i in range(10):
doc = {
"id": i,
"message": f"Random message {i}",
"value": random.randint(1, 100),
"timestamp": time.strftime("%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S")
}
try:
response = client.index(index=index_name, document=doc)
print(f"Document written, ID: {response['_id']}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error writing document: {e}")
# Example: Read 10 documents
print("Reading data...")
try:
response = client.search(index=index_name, query={"match_all": {}}, size=10)
print(f"Search results: {len(response['hits']['hits'])} documents")
for hit in response['hits']['hits']:
print(hit['_source'])
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error reading documents: {e}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()